Last updated on 13th June 2024
In this article we’re going to take a look at the 10 best project management techniques for project managers in 2024.
Project management impacts everyone. It doesn’t matter what industry you’re in, how big your business is, or how many clients you have, everybody should be managing projects efficiently in order to be as successful as possible.
So, let’s take a look at the 10 best project management techniques to see if we can improve this for your business in 2024.
1. Kanban
What is Kanban?
Kanban is a visual project management technique that was first implemented by engineers at Toyota to improve manufacturing efficiency. Kanban (看板) is a Japanese term that when translated means ‘sign board’.
The name derives meaning from the visual boards that are used in Kanban to give team members a better grasp of their workflow.
How does Kanban work?
Kanban is one of the simplest project management techniques out there. It’s really easy to get started and can be applied to most projects.
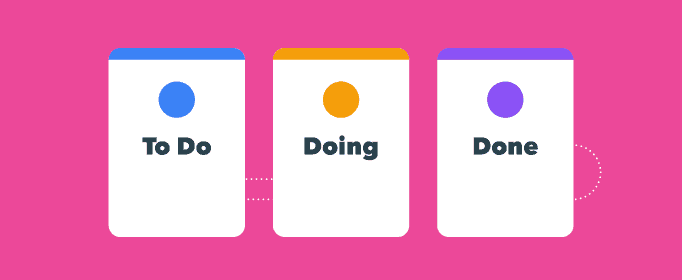
The idea is to break complex projects down into smaller tasks and split these tasks into different columns. The standard kanban technique uses 3 columns: To-do, Doing, and Done. However, you can rename these to fit your business. For example, if you were managing marketing projects then you might change the columns to better reflect your specific workflow, like this:

As tasks dependencies are moved along the workflow, the project progresses. The project is complete when every task is in the ‘Done’ column.
Who should use Kanban?
Anyone can use kanban! It’s especially great for projects that require cross-team collaboration as it allows everyone involved in the project workflow to get a quick, visual overview of tasks and understand where potential bottlenecks may occur.
Benefits of Kanban
The visual and transparent nature of kanban makes managing projects easier. It allows teams to focus on their own work while at the same time gain an understanding of the bigger picture. This can be really motivating and can certainly help projects to run more smoothly, giving you a better chance of hitting your project deadline.
2. Critical Path Method (CPM)
What is the Critical Path Method?
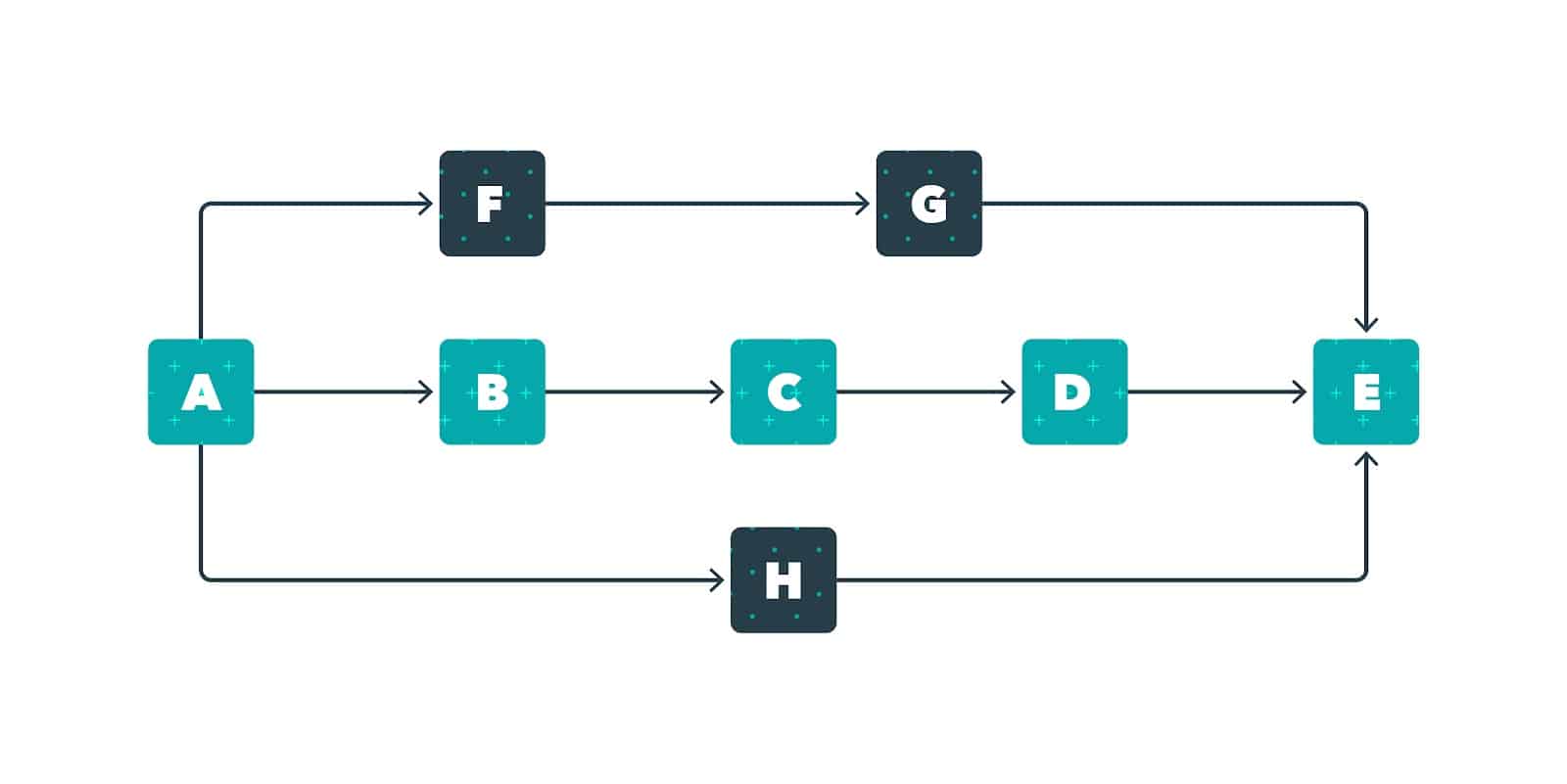
The Critical Path Method (CPM) is a project management technique that helps you manage your project efficiently by calculating the shortest route to project completion.
In other words, you identify all of the tasks required to complete the project and then map those out so that you can schedule your project in the most productive way and get an accurate timeline.
How does the Critical Path Method work?
The first thing you need to do is look at the project scope. Start by making a list of all the tasks that need to be completed over the course of your project. Then, identify tasks that can be completed in tandem and dependent tasks (tasks that need to run one after the another). For example, if you’re managing an animated video project, you can’t start work on the storyboard without first completing the script. However, you could probably record the voiceover and work on the storyboard at the same time (seeing as your script will be complete).
This exercise will help you to create an accurate schedule for your project and give you an idea of how long everything will take to complete.
Who should use the Critical Path Method?
This project management technique is best for large scale, complex projects that span many teams, especially if you have a lot of dependent tasks that need to be completed before you can move onto the next step.
Benefits of the Critical Path Method
By giving you and your team a clear roadmap to follow, the Critical Path Method (CPM) helps you deliver complex projects on time, and with improved accuracy. It’s also great for keeping stakeholders happy because it allows you to define the project scope upfront and share a projected timeline for project completion.
3. PERT
What is PERT?
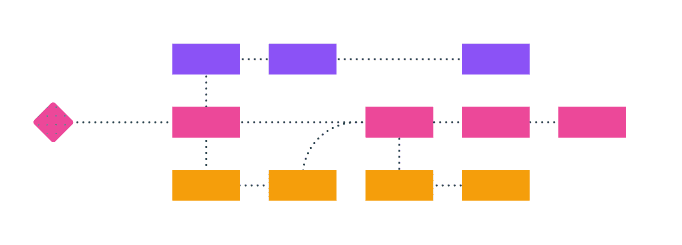
PERT stands for program evaluation and review technique. It’s a graphical representation of a project’s duration, that also displays all of the tasks necessary to complete the project.
In this sense, it’s similar to the Critical Path Method. The biggest difference is that PERT applies different calculations and time estimates to give a more accurate prediction of when a project is likely to be completed.
How does PERT work?
When implementing the PERT technique, you usually start with your deadline and work backwards. Like the Critical Path Method, you’ll make a list of all of your tasks. The biggest difference is adding estimated durations to each task.
It’s recommended that you calculate 3 scenarios:
– The most likely/realistic amount of time it will take
– The longest/pessimistic amount of time it could take
This will help you to more accurately predict how long your project will take, giving you best and worst case scenarios.
Who should use PERT?
PERT is for the same types of projects as the Critical Path Method, so large scale affairs that span many teams. PERT is better for projects that have strict, unmovable deadlines.
Benefits of PERT
PERT gives you a clear path to follow and makes tracking a project’s progress a lot easier and more accurate. Another benefit of PERT is that it helps you deliver projects on time and on budget and, well, who doesn’t want that?!
4. Scrum
What is Scrum project management?
As a project manager, you’ve probably heard of agile project management before. It’s a way to manage projects by breaking them down into smaller phases. There are different facets of agile project management and one of those is Scrum.
Scrum project management is a technique that revolves around teamwork and accountability by focusing on iterative progress towards a well-defined goal.
How does Scrum work?
Projects are broken down into small increments called ‘Sprints’. Sprints typically last around 2 weeks, and during this time teams will work on a particular deliverable.
There’s also usually daily stand up meetings that are designed to be quick check-ins, perhaps 10 minutes or so, to keep everyone pushing in the right direction.
After each 2 week sprint, a longer review meeting is held so that the project team can share suggestions for what everyone should work on during the following sprint. This process repeats for the entirety of the project life cycle!
Who should use Scrum?
Scrum is often used for software development projects, as these are liable to change. However, it can be applied to any project where the focus is more on “getting things right” rather than “getting things finished”. In other words, Scrum is great for projects where there’s no time pressure or deadline.
Benefits of Scrum
It’s one of the more freeing project management techniques, with creativity openly encouraged. It’s collaborative and also allows stakeholders to get regular updates on progress.
5. Waterfall
What is Waterfall project management?
Like Scrum, Waterfall is another sub-framework of agile project management. The difference is that while Scrum breaks down projects into sprints and is flexible with how long the process can take, waterfall project management breaks projects down into linear sequential phases.
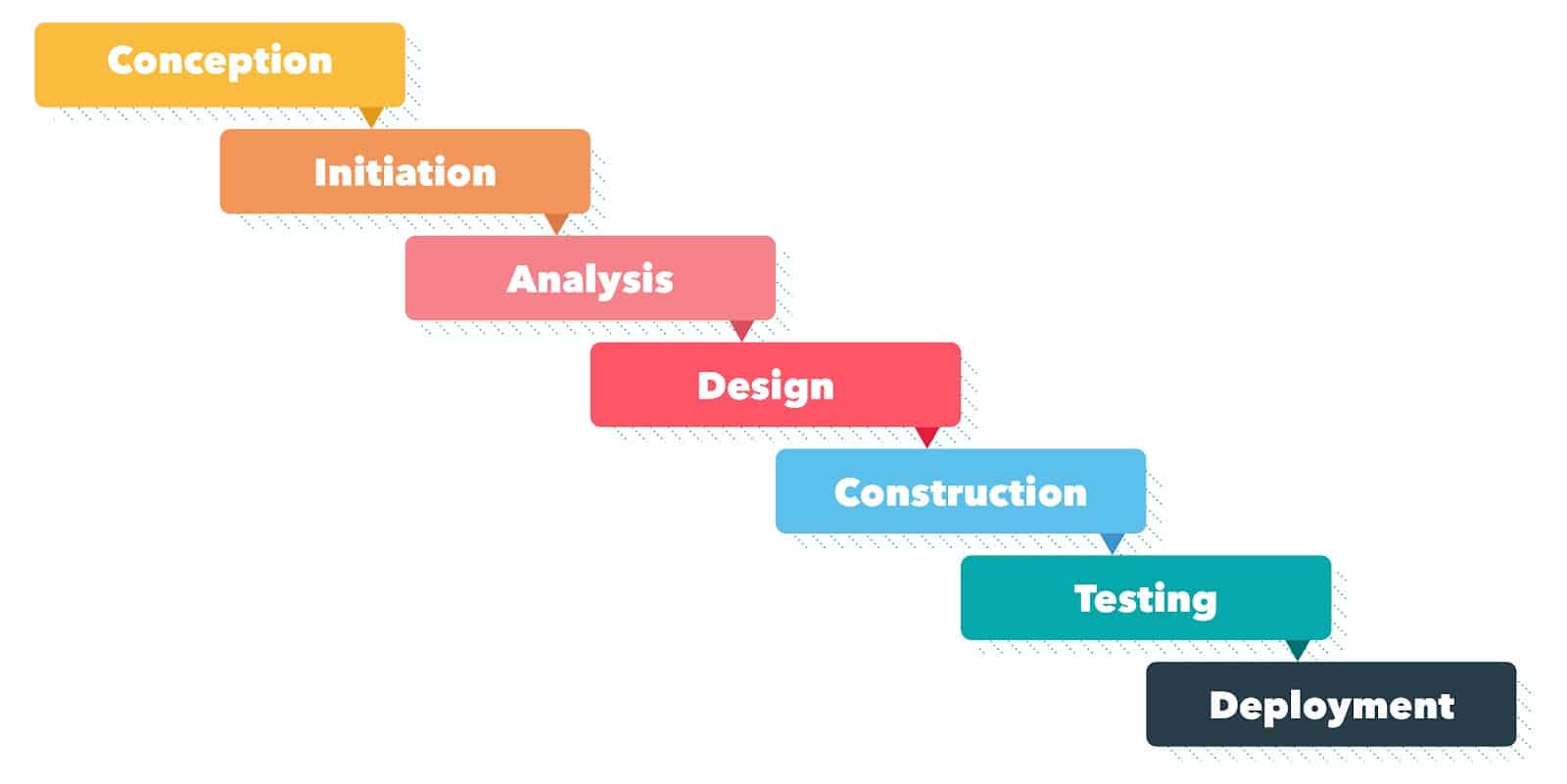
How does Waterfall work?
Typically, projects are broken down into 5-7 steps:
– Initiation
– Analysis
– Design
– Construction
– Testing
– Deployment
Each step needs to be completed before you can move onto the next one, and because everything is mapped out at the beginning of the project there’s little to no room for error.
To keep things on track, an important aspect of waterfall project management is documentation. Before moving ahead to a new step, a comprehensive review should take place. This is so the project team can document everything that happened, particularly anything of importance for future steps.
Who should use Waterfall?
Waterfall project management is best for projects where the end goal is clearly defined and stakeholders know exactly what they want. Waterfall is not for projects that are likely to change and require flexibility – so, while they can both be filed under ‘agile project management methodology’, in some ways Waterfall is the complete opposite of Scrum!
Benefits of Waterfall
While it may seem like a rigid project management technique (and it is), this has benefits too. Waterfall projects are easy to monitor and track, because expectations are clear from the outset and there’s a lot of documentation.
This documentation also makes waterfall a great project management technique for companies working in highly regulated industries.
6. Gantt
What is Gantt?
Gantt charts are another visual project management technique that allow you to track the amount of work that’s required to be completed over time. Gantt charts have been in use for over a century, but are still relevant today because they are so easy to implement.
How does Gantt work?
A Gantt chart is like a stacked bar chart. Data can vary, but usually there’s project tasks on a vertical axis and timelines representing task duration on a horizontal axis.
This makes it very easy to see – at a glance – things like: who is working on what task, task start and end dates, task dependencies, and how long the project is likely to take overall. By using a Gantt chart to monitor project progress, you can spot what actions you need to take (if any) to ensure you stay on schedule.
Who should use Gantt?
Anyone. This technique can be applied to pretty much any project, and it can also be used in conjunction with other project management techniques.
Benefits of Gantt
The main benefits are that Gantt charts are visual and easy to implement, and you can determine project progress at a glance.
7. Work Breakdown Structure
What is the Work Breakdown Structure?
Work Breakdown Structure (sometimes referred to as WBS) is a simple project management technique that does exactly what it says on the tin – breaks large projects down into smaller, more manageable sections of work.
An example would be if you were building a house. That’s a mammoth task and could be quite overwhelming at first. WBS helps you break it down. So, you’d start by laying the foundations, then you’d do the brickwork, then fit windows and doors, and so on, until you have a completed house.
How does Work Breakdown Structure work?
Like with PERT, it’s good practice to start at the end. So if you were building a house then a completed, liveable house is the end goal. From there you can work backwards to list out all of the tasks required to get you there.
Assign a task to each deliverable, and then break each task down into a number of sub-tasks, until you can’t break them down any further. This will help to make your huge project more manageable.
Who should use Work Breakdown Structure?
This is best for those huge, complex projects that you feel are almost too daunting to start. Breaking your workload down into smaller chunks can really help you get moving.
Benefits of the Work Breakdown Structure
WBS allows you to visualise the entire project scope and keep all of your tasks organised, while also ensuring your project moves forward steadily and with ease.
8. Lean

What is Lean project management?
As you can probably guess from the name, Lean focuses on maximising value and minimising waste. It’s a project management technique that helps you optimise your team and resources while providing as much value as you can to the end customer.
How does Lean work?
Waste is grouped into 3 categories: Muda, Mura, Muri. This project management technique is also Japanese, like Kanban, hence the Japanese names.
Muda means wastefulness. It refers to activities that don’t add value, such as transporting goods from one location to another (excessive movement of product). Mura means unevenness, and refers to processes that create bottlenecks. For example, if one team is moving a lot slower than another team and creating a hold up.
Finally, Muri means overburden. In other words, burnout.
Burnout can be caused by stress, poor organisation, or anything else that prevents people from being able to do their best work.
To implement lean project management, simply create a table with 3 columns labelled muda, mura, and muri, and then divide up the processes in your business that you think are wasteful. From there, you can work through suitable solutions.
Who should use Lean?
Lean has its origin in car manufacturing, like Kanban, so it’s perfect for businesses in the manufacturing industry. But it could also work for anyone wanting to maximise output and minimise waste.
Benefits of Lean
Lean helps you to shift your focus so that you can concentrate on saving money, reducing waste, and delighting customers.
9. Six Sigma
What is Six Sigma?
Six Sigma is a highly structured project management technique that focuses on defect reduction and reducing variation. It got its start in Motorola (in the mid 80s) and has been adopted by many businesses since then, including General Electric.
To sum it up in short, Six Sigma is all about reducing variation, which is why it’s proved so popular in the manufacturing industry (and not so much for software development projects.)
The goal of the Six Sigma methodology is, quite simply, a defect-free process. This means that, in contrast to agile methodologies which promote iteration and creative variation from stakeholders throughout the process, Six Sigma is a highly structured methodology. It prizes organisation, efficiency and scientific data at each stage, since the end goal is precision and reliability.
How does Six Sigma work?
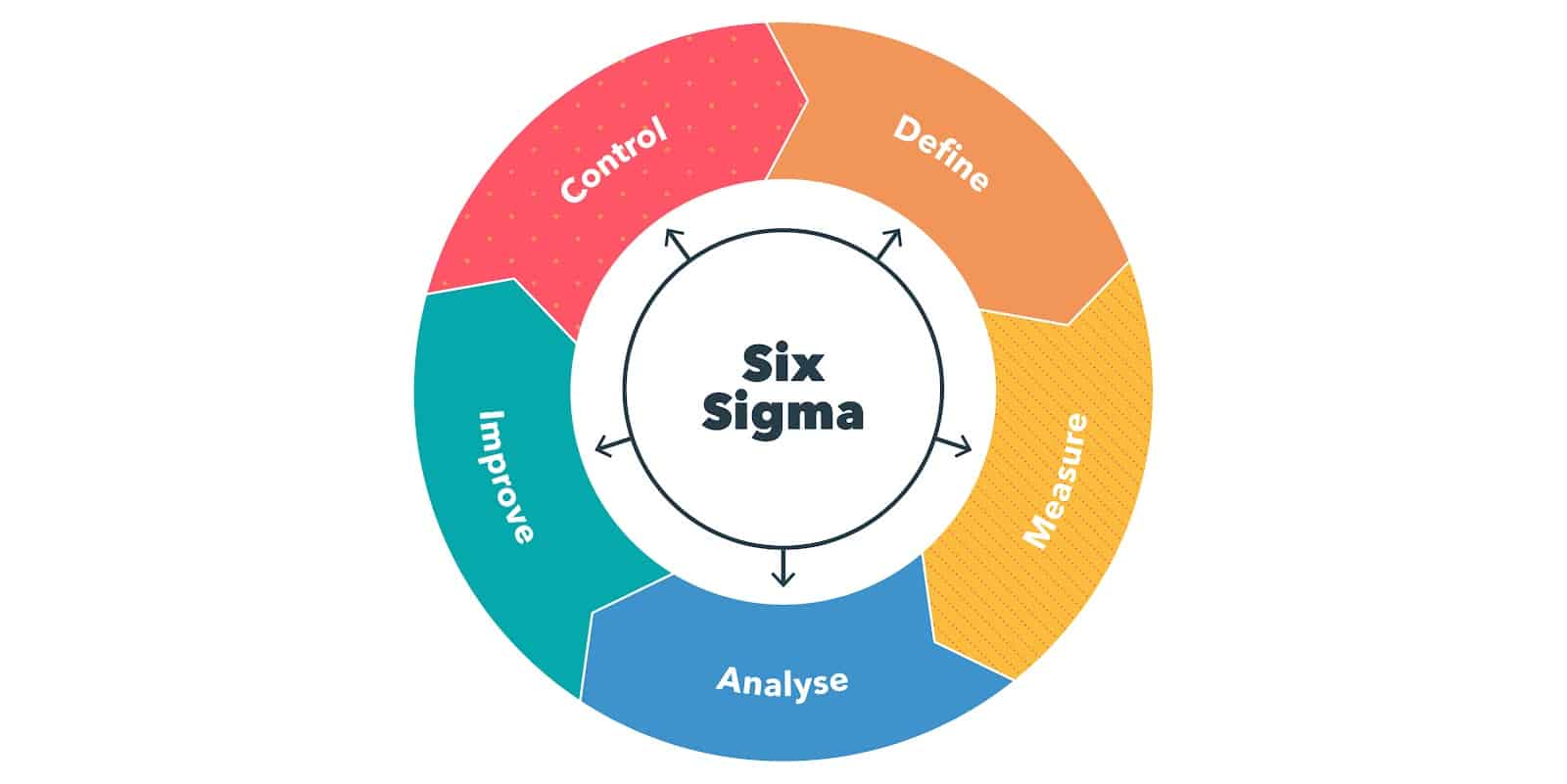
The goal of Six Sigma is to have a defect-free process. There are 5 key phases used to achieve this:
2. Measure
3. Analyse
4. Improve
5. Control.
These are sometimes known by their acronym DMAIC.
Six Sigma can be easily implemented by following these phases. The first phase, define, is all about defining the scope of the project or identifying the problem you’re trying to solve. Then you measure your current process and/or capabilities, and analyse the data collected. From there, you work to improve performance based on the data. The last phase, control, is all about implementing your new and improved process.
Who should use Six Sigma?
Six Sigma is best for teams that are looking for a structured principle that can be applied to various different projects within the business.
Benefits of Six Sigma
Six Sigma is great because it helps businesses to reduce waste and create more predictable project outcomes. As a result of this, you’re also likely to benefit from an increased chance of project success.
10. Rapid Application Development (RAD)
What is RAD?
The aim of RAD is to facilitate faster software development. This project management technique puts less emphasis on planning and more emphasis on doing.
The idea is to develop applications as rapidly as possible by gathering continuous feedback and using that to develop frequent iterations of a software. The need for RAD came from the increasingly competitive market of software development.
How does RAD work?
RAD project management is usually broken down into cycles that run on repeat. Each cycle begins by defining your project requirements. From there, you create and release a prototype to a defined number of users.
Then you’ll gather feedback from those users and use that to create a new iteration of your software – thus repeating the process!
Who should use RAD?
RAD was created for software development teams. It’s perfect if you want to push a working model of your app out to customers ASAP, even if there are some flaws.
Benefits of RAD
The main benefit, as the name suggests, is that it’s quick. You also benefit from user feedback which can be invaluable to your app. Plus, there’s less planning involved so you can just get stuck in and run with your ideas.
Final thoughts
Whatever type of project you’re working on, there’s a project management technique out there that can help you.
Another thing that all project managers need is a reliable project management software, like Project.co.
Project.co gives you all of the project management tools you need in one place. You can manage an unlimited number of projects, easily collaborate with team members and clients, and keep your projects on track with complete visibility of progress.